12 emails! I’ve gotten 12 emails about the Gastric bypass article on here. A couple saying it’s cheating, one saying it’s a hoax and the rest asking for some more science behind the surgery, so here it is.
Gastric bypass surgery has traction as a successful method for combatting obesity and related health issues. The procedure involves manipulating the digestive system, limiting food consumption and nutrient absorption. Nevertheless, the intricacies of this surgery necessitate extensive comprehension of human physiology and metabolism.
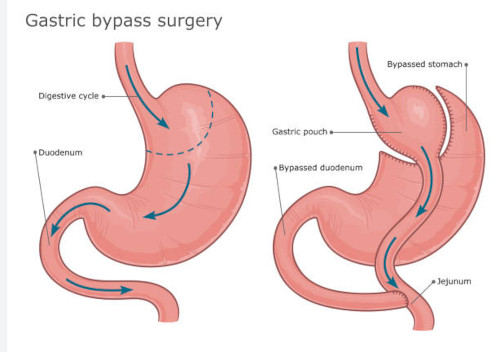
The study of the structure and function of the digestive system
Prior knowledge of the digestive system’s anatomy plays a vital role in comprehending the mechanism behind gastric bypass surgery. This intricate system comprises various organs and tissues that collaborate to facilitate the conversion of food into usable energy and nutrients that promote physical development.
Food ingestion commences with mastication in the oral cavity, followed by blending with saliva, and then proceeds through the esophagus to the gastric chamber.
The small intestine is more than 20 feet long in adults, and it receives food from the stomach. The stomach uses hydrochloric acid and enzymes to mix and churn the food, breaking down proteins, carbohydrates, and fats.
Within the small intestine lies the principal location for nutrient absorption. This is made possible due to the minute, protruding villi that cover the intestine walls, multiplying the surface area accessible for nutrient absorption.
The large intestine is responsible for absorbing water and electrolytes and eliminating waste products as feces after the food passes through the small intestine. Hormones and the nervous system play a crucial role in regulating the digestive system by controlling the release of digestive juices and muscle contractions in the digestive tract.
Insights into the Process of Shedding Pounds
The objective behind gastric bypass surgery is to curtail the amount of food ingested while decreasing nutrient intake, resulting in reduced weight. The approach employed by gastric bypass surgery to accomplish this comprises numerous means.
To begin with, gastric bypass surgery is a procedure that entails developing a tiny pouch in the upper part of the stomach. This pouch limits the quantity of food that can be ingested in a single instance. After that, the pouch is linked to the small intestine, thereby circumventing the other portions of the stomach and duodenum situated in the small intestine.
The primary location where nutrients get absorbed is the duodenum, therefore, this bypass minimizes the assimilation of carbs and fats.
One could say that gastric bypass surgery has a profound impact on the hormones that play a role in regulating hunger and the feeling of being full. These hormones, which are generated by the small intestine, include ghrelin, which encourages hunger, as well as peptide YY and glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1), which diminish hunger and increase the sensation of fullness. As a result of gastric bypass surgery, ghrelin levels tend to decrease while peptide YY and GLP-1 levels tend to rise, which results in a reduction in hunger pangs and an augmented sense of being full.
The alteration of the gut microbiome is one of the significant changes that occur after undergoing gastric bypass surgery. These bacterial communities inhabit the digestive system, and they perform vital roles in metabolism and immune function. Due to their impact on the body, the gut microbiome has been associated with obesity and other metabolic disorders.
Following gastric bypass surgery, an alteration occurs in the gut microbiome, causing a decline in the prevalence of bacteria connected to obeseness and an augmentation in the prevalence of bacteria linked to maintaining a healthy weight.
Health consequences that occur over an extended period of time
It has been proven that gastric bypass surgery can be a successful method in treating obesity and its related ailments, including sleep apnea, high blood pressure, and type 2 diabetes. Nonetheless, it’s crucial to take into account the possible long-term consequences to health.
Gastric bypass surgery can have a major impact on nutrient absorption in the long run. This is especially true for fat-soluble vitamins and minerals, resulting in deficiencies in vital nutrients like iron, calcium, and vitamin B12. These deficiencies can contribute to a plethora of health concerns like osteoporosis, nerve damage, and anemia.
Gastric bypass surgery patients are generally recommended to take supplements containing vitamins and minerals throughout their lifetime in order to avoid any deficiencies.
Dumping syndrome could be a possible lingering outcome of gastric bypass surgery where food travels hastily from the stomach to the small intestine. Unfavorable indications including queasiness, heaving, the runs, and lightheadedness usually arise, especially if one feeds on foods that are high in fat or sugar. In order to circumvent dumping syndrome, patients must consume small, regular meals that have low sugar and fat content.
The psychological ramifications of gastric bypass surgery are notable and may affect one’s emotional state, self-confidence, and perception of their physical appearance. Although many individuals see a positive shift in their mental well-being and overall lifestyle, there are those who may develop distorted body images or feelings of insufficiency. As such, it is crucial for patients to receive guidance and assistance to confront these concerns pre- and post-operation.
Gastric bypass surgery entails a possibility of complications such as infection, bowel obstruction, and bleeding. These risks are more pronounced in patients who are advanced in age or have other existing medical conditions or have a high body mass index. Patients must exercise due diligence in choosing a competent and proficient surgeon and should thoroughly weigh the potential risks and advantages prior to making a decision.
End result
The treatment for obesity and its related health issues, known as gastric bypass surgery, is intricate but impactful. This procedure limits food consumption and nutrient absorption which results in weight reduction and an improvement in metabolic well-being. However, its benefits come with long-term drawbacks such as malabsorption of vital nutrients, the occurrence of dumping syndrome, harmful psychological effects, and medical complexities.
Before deciding to undergo gastric bypass surgery, patients must thoroughly evaluate the potential advantages and drawbacks of the procedure. Working closely with their healthcare team is crucial to achieving the most favorable results.


Lämna en kommentar